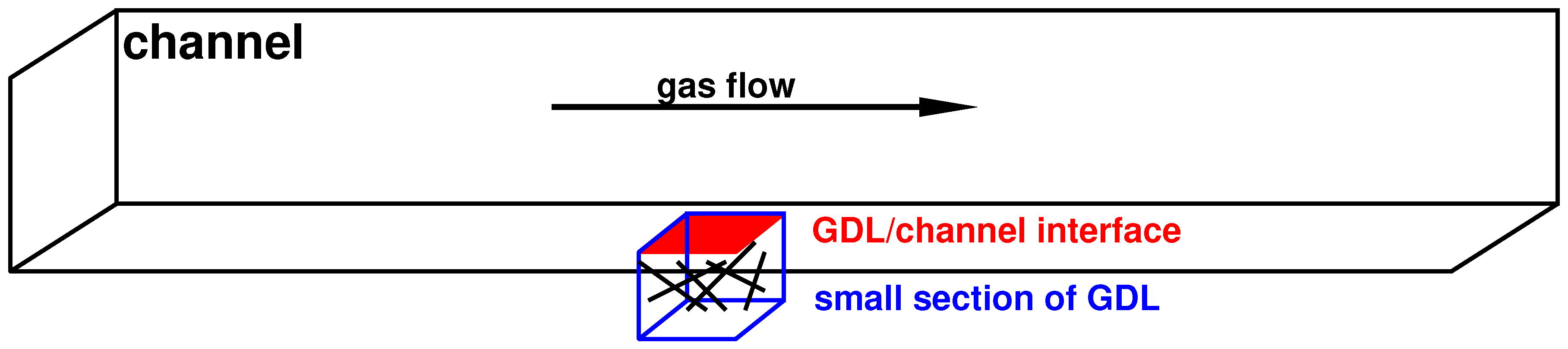
Gas transport with molecular sieving properties was achieved through the nano channels formed by the go interlayer spaces which would be affected by the activated diffusion and preferable adsorption.
Gas diffusion with nitrogen through ceramic.
The adsorption rate of a gas becomes the slower for msc with the smaller pore size and the temperature also governs the rate of adsorption of a gas because of the activated diffusion of adsorbate molecules in.
The highest rates were for fused silica and vycor brand glass.
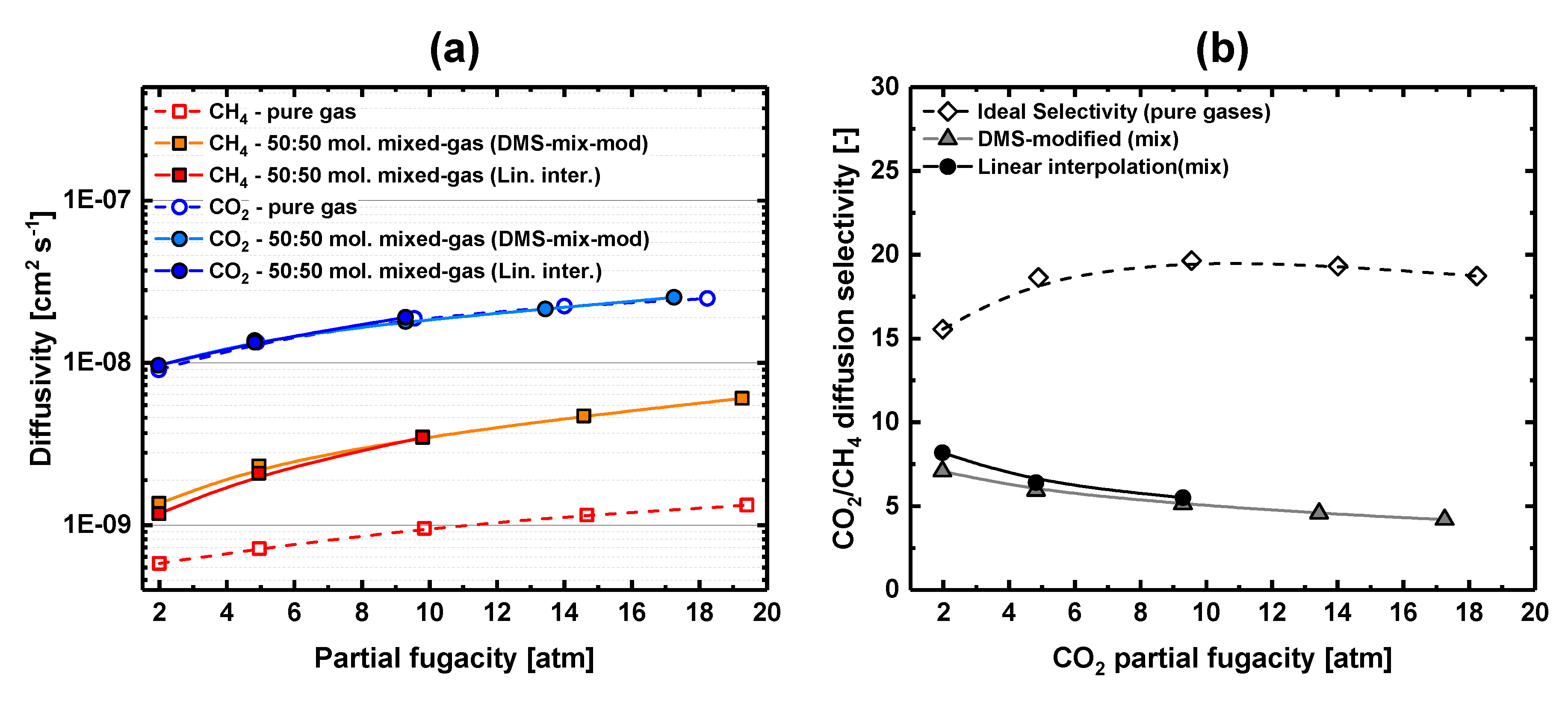
Nitrogen n 2 and carbon dioxide co 2 was measured at a temperature of 450 c and feed pressures between 0 85 up to 1 0 bar.
It was the first process to be developed that was capable of.
Jacers is a leading source for top quality basic science research and modeling spanning the diverse field of ceramic and glass materials science.
The temperature range covered was from 80 to 600 c.
The membrane used in the process is a generally non porous layer so there will not be a severe leakage of gas through the membrane.
Membrane morphological characterization can be achieved through some notable methods such as scanning electron microscope sem bubble point technique mercury porosimetry and nitrogen gas adsorption desorption.
Gas separation across a membrane is a pressure driven process where the driving force is the difference in pressure between inlet of raw material and outlet of product.
Dm d grad c df dt.
Using the mass spectrometer as an analytical tool and as a means of rate measurement the rates of helium diffusion through nine types of glass were measured.
Selectivity of 2 7 was obtained for he n 2 at 1 bar.
The adsorption rate of gas molecules such as nitrogen oxygen hydrogen and ethylene depends strongly on the pore size of msc.
Using the mass spectrometer as an analytical tool and as a means of rate measurement the rates of helium diffusion through nine types of glass were measured.
Diffusion coefficient is the proportionality factor d in fick s law see diffusion by which the mass of a substance dm diffusing in time dt through the surface df normal to the diffusion direction is proportional to the concentration gradient grad c of this substance.
Gaseous diffusion is a technology used to produce enriched uranium by forcing gaseous uranium hexafluoride uf 6 through semipermeable membranes this produces a slight separation between the molecules containing uranium 235 235 u and uranium 238 238 u.
Observation of the permeance of the alumina support revealed that the transport of the gases under these conditions is governed by knudsen diffusion.
Hence physically the diffusion coefficient implies that the mass of the substance diffuses through a.
The gas permeability through porous media of hydrogen helium and a number of inert gases of potential interest n2 ne ar kr xe has been assessed via the models of knudsen and poiseuille.
In essence gas transport through porous ceramic membrane pores can be obtained based on the kinetic theory of gases.