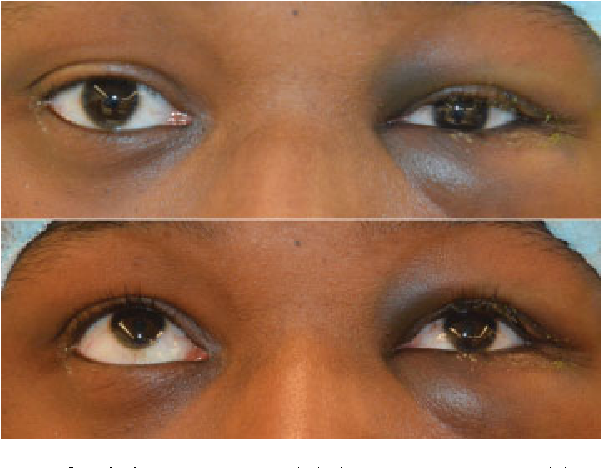
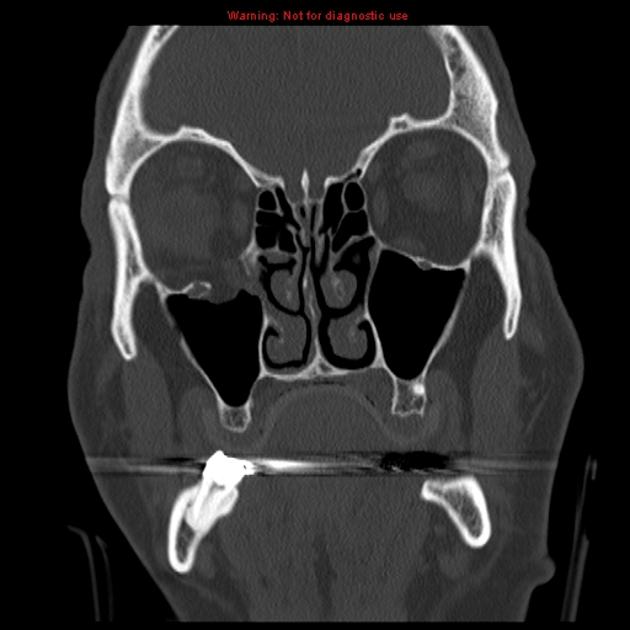
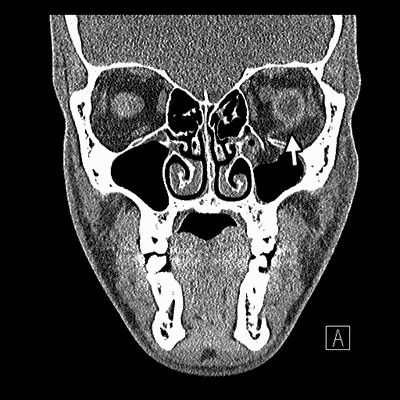
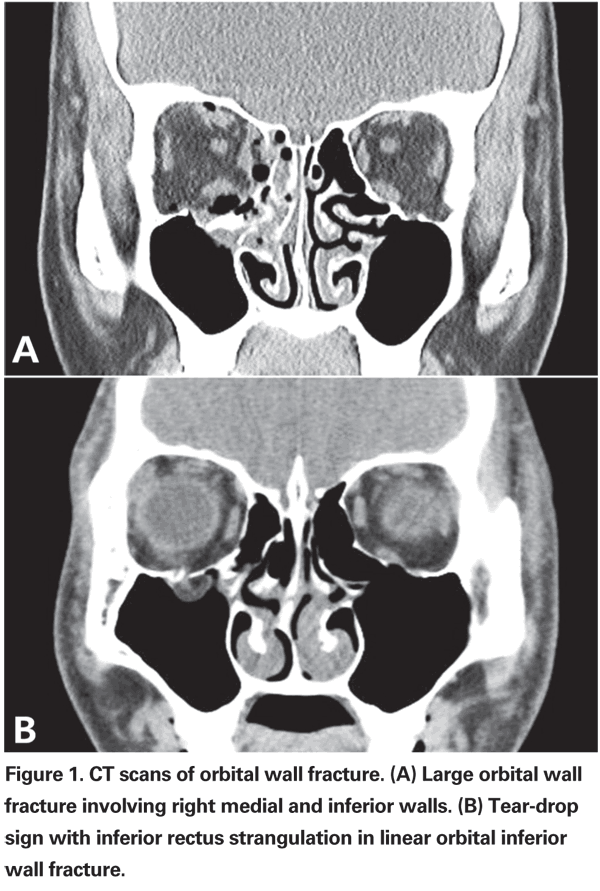
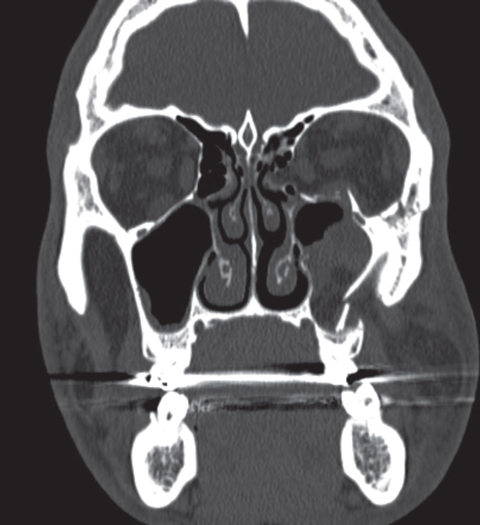
This report describes the case of a patient in his 40s with a large right orbital floor and medial wall fracture without radiographic evidence of extraocular muscle compression or entrapment who developed severe nausea and bradycardia with movement of his affected eye.
Fractured orbital floor with ocular muscle entrapment.
Pediatric orbital floor fracture.
Orbital floor fractures may result when a blunt object which is of equal or greater diameter than the orbital aperture strikes the eye or on the cheek 1.
For example a fracture might be described as a pure inferior blowout fracture with likely entrapment.
The principal morbidity associated with orbital fractures is eye injury.
With the trapdoor variant there is a high frequency of extra ocular muscle entrapment despite minimal signs of external trauma a phenomenon referred to as a white eyed.
Especially when the fracture is into an.
Orbital floor fracture also known as blowout fracture of the orbit eye socket.
Harris gj garcia gh logani sc murphy ml.
Correlation of preoperative computed tomography and postoperative ocular motility in orbital blowout fractures.
The most commonly entrapped material following a blowout fracture is orbital fat this alone may lead to decreased up gaze if the orbital floor is involved.
Rarely if ever is performing a forced duction test necessary or informative in making the diagnosis of extraocular muscle restriction in an awake patient with an orbital blowout fracture.
Hawes mj dortzbach rk.
This is indicated by inability to move the eye in upward gaze or sometimes downward gaze and one may observe autonomic instability the oculocardiac reflex.
Direct extraocular muscle involvement.
Getting hit with a baseball or a fist often causes a orbital blowout fracture.
Associated injuries include corneal abrasion lens dislocation iris disruption choroid tear scleral tear ciliary body tear or bruise retinal detachment and tear hyphema ocular muscle entrapment and globe rupture.
Due to extraocular muscle entrapment.
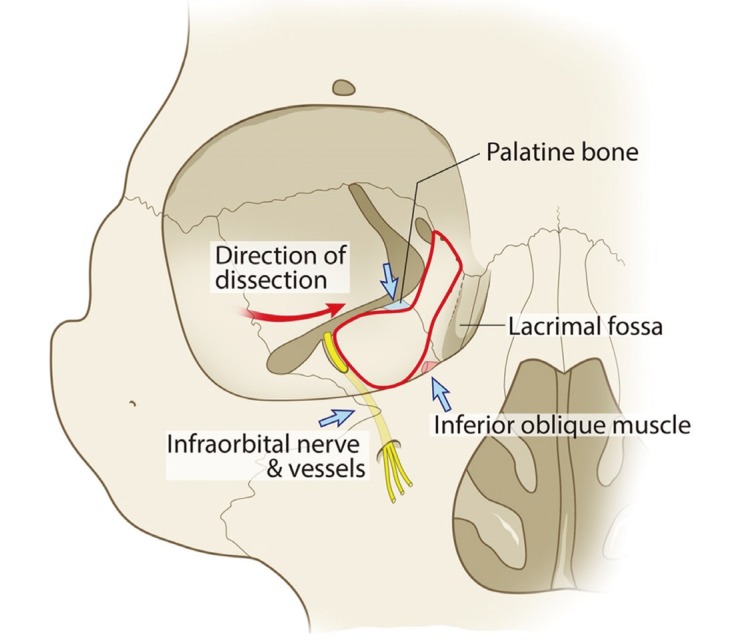
Most fractures occur in the floor posterior and medial.
The fracture may spring back into place see trapdoor fracture.
Ophthal plast reconstr surg.
Other causes can include direct damage to the extraocular muscles during the injury disruption of motor nerve branches or commonly swelling and hemorrhage within the orbit causing limitation in.
Immediately after an orbital floor fracture the affected eye may have impaired.
Males are at higher risk of eye injuries because of their increased incidence of trauma.
In pure orbital blowout fractures the orbital rim the most anterior bony margin of the orbit is preserved while with impure fractures the orbital rim is also injured.
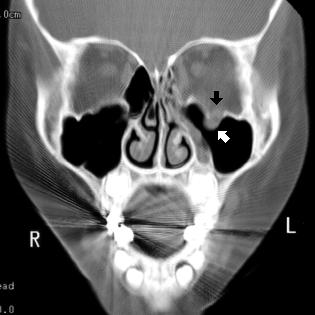
The most common muscle to be entrapped by the fracture is the inferior rectus muscle.
Large orbital fractures in older patients are infrequently associated with an exaggerated oculocardiac reflex.
Extraocular muscle entrapment from orbital floor fracture in a child.




.jpg)