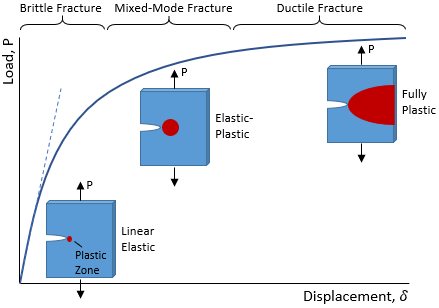
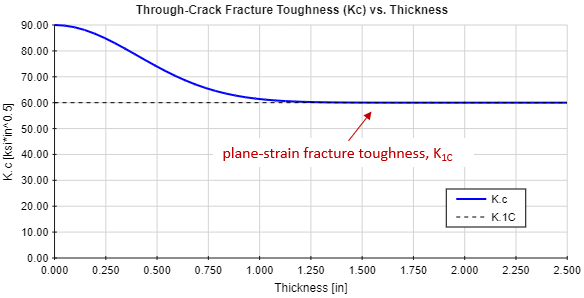
Ceramics have a lower fracture toughness but show an exceptional improvement in the stress fracture that is attributed to their 1 5 orders of magnitude strength increase relative to metals.
Fracture toughness of ceramics griain size.
The dependence of mechanical properties of 3y tzp ceramics on their grain sizes in the range from 0 19 µm to 2 15 µm has been investigated.
On the other hand the apparent fracture toughness with slow crack growth increased with increasing grain size due to the r curve behavior.
The fracture toughness of zirconia alumina and silicon nitride ceramics zirconia and alumina single crystals silicon carbide as well as silicon nitride ceramic particulate composites silicon nitride laminated composites and other ceramics materials were studied by a single edge v notched beam sevnb method.
In this study by analyzing the fracture measurements of eight different notched ceramics with an average grain size g of 3 40 μm a simple model describing the relation between the notch fracture toughness and fracture toughness.
The static fatigue crack growth rate was reduced with increasing grain size.
The fracture toughness of alumina ceramics of different grain sizes were determined by the surface crack in flexure method.
The fracture toughness of composites made by combining engineering ceramics with engineering polymers greatly exceeds the individual fracture toughness.
The hardness decreased with increasing grain size.
Vickers indentation and single edge v notched beam sevnb techniques have been used to measure hardness and fracture toughness respectively.
Room temperature fracture toughness and hardness of spark plasma sintered pure b 4 c ceramics with grain sizes ranging from 120 nm to 17 μm have been studied.
Rather it increases with the notch root radius ρ in a notched specimen.
Although vickers indentation is a popular simple and quick method to determine the fracture toughness it is also controversial so the surface crack in flexure method published in 2007 as astm standard c1421 01b was used to determine the fracture toughness.
The fracture toughness was almost constant for ceramics with the grain size up to 0 40 μm and then grew with increasing grain size up to 7 8 mpam0 5 for ceramics with grain size of 1 8 μm.
A review of the fracture energy and toughness data for dense ceramics at 22 c shows maxima commonly occurring as a function of grain size.
Kishi matrix grain size effect and fracture bmamor on bending strength and fracture toughness in multi toughened al2o3 proceedings of the 16th annual conference on composites and advanced ceramic materials.
The bending strength increased with decreasing grain size.
Vickers indentation tests were used to determine hardness and fracture toughness.
The validated fracture toughness is independent of grain size.
Such maxima are most pronounced for non cubic materials where they are often associated with microcracking and r curve effects especially in oxides but often also occur at too fine a grain size for association with microcracking.