F which represents force k which is called the spring constant and measures how stiff and strong the spring is and x is the distance the spring is stretched or compressed away from its equilibrium or rest position.
Force of spring attached to floor.
The string s tension is measured.
Normal force n is the force that pushes up against an object perpendicular.
The variables of the equation are.
The graph in figure q8 10 shows the tension in the spring as a function of the spring s length l.
The motion of a mass attached to a spring is an example of a vibrating system.
Spring force f spring.
In physics when frictional forces are acting on a sloped surface such as a ramp the angle of the ramp tilts the normal force at an angle.
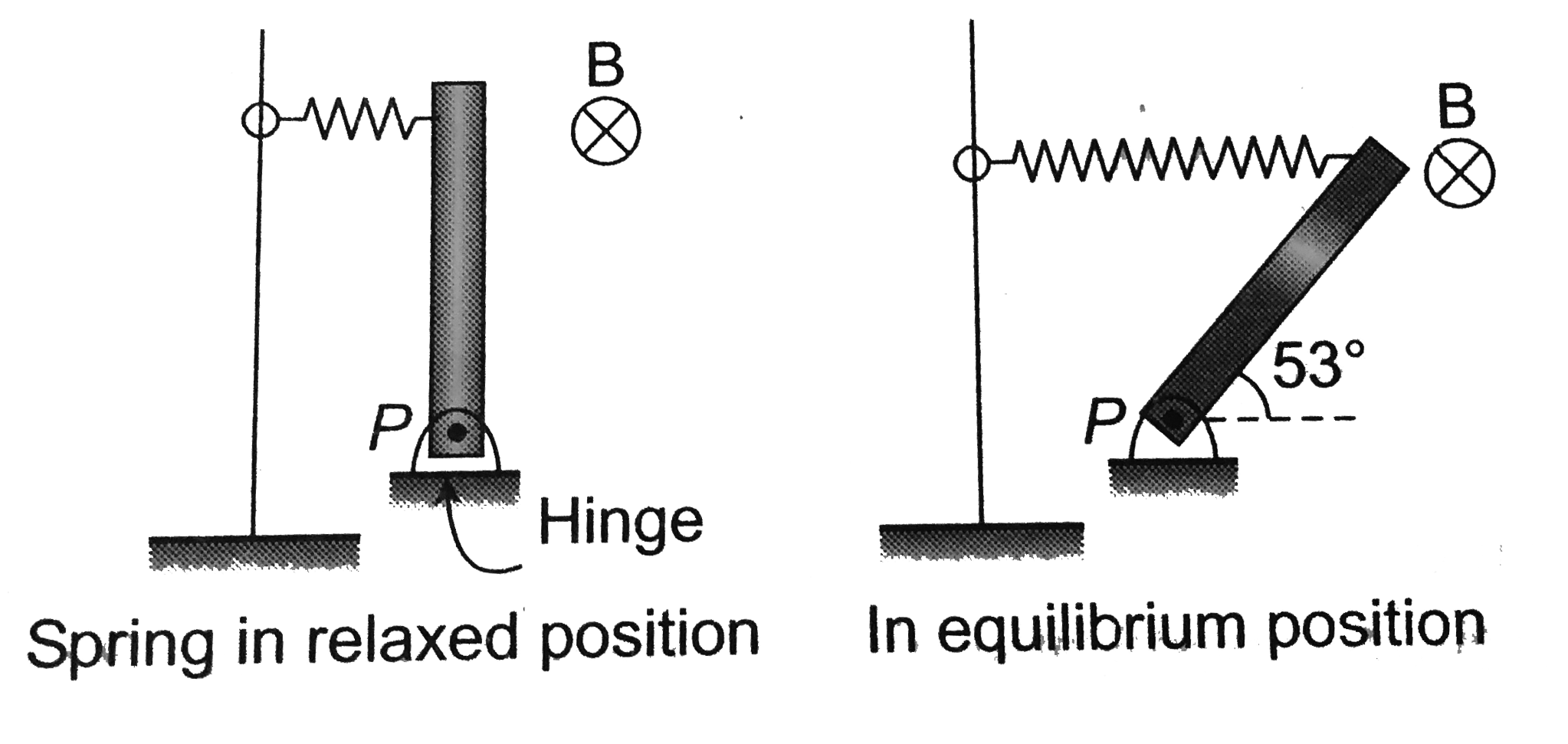
A spring is attached to the floor and pulled straight up by a string.
The minus sign shows that this force is in the opposite direction of the force that s stretching or compressing the spring.
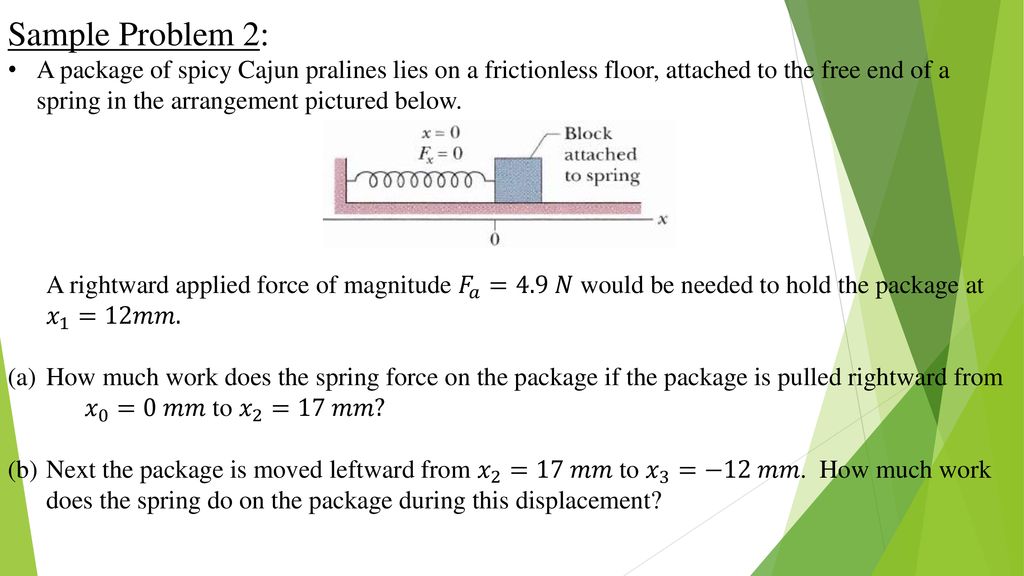
A 4 00 kg block sitting on the floor is placed against the spring.
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the floor is uk 0 400.
If it is stationary then the force of the spring will equal the force of gravity mg kx.
The spring is holding it up.
The block and spring are released from rest and the block slides along the floor.
F has magnitude of 82 0 n and is directed toward the wall.
What is the spring constant.
The string s tension is measured.
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the block is 0 42.
If a spring is stretched then a force with magnitude proportional to the increase in length from the equilibrium length is pulling each end towards the other.
In this lesson the motion of a mass on a spring is discussed in detail as we focus on how a variety of quantities change over the course of time.
The spring has force constant 900 n m.
If a spring is compressed then a force with magnitude proportional to the decrease in length from the equilibrium length is pushing each end away from the other.
When you work out the frictional forces you need to take this fact into account.
A 10 n m b 25 n m c 50 n m d 100 n m.
The force exerted by a spring is f kx k is the spring constant and x is the distance the spring is compressed or stretched beyond its resting position.
You apply a constant force f is directed toward the wall.
Such quantities will include forces position velocity and energy both kinetic and potential energy.
A spring is attached to the floor and pulled straight up by a string.
A ideal spring has an equilibrium length.
As an example consider pushing a box across a floor.
The spring force is the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it.
A 2 95 kg block on a horizontal floor is attached to a horizontal spring that is initially compressed 0 0330 m.